Coronavirus continues to spread globally, and more recently, in the Middle East.
Talk to one of our doctors today for a risk assessment and tips on how to protect yourself.
COVID-19 – Around The World
COVID-19 – Latest News
COVID-19 – Facts
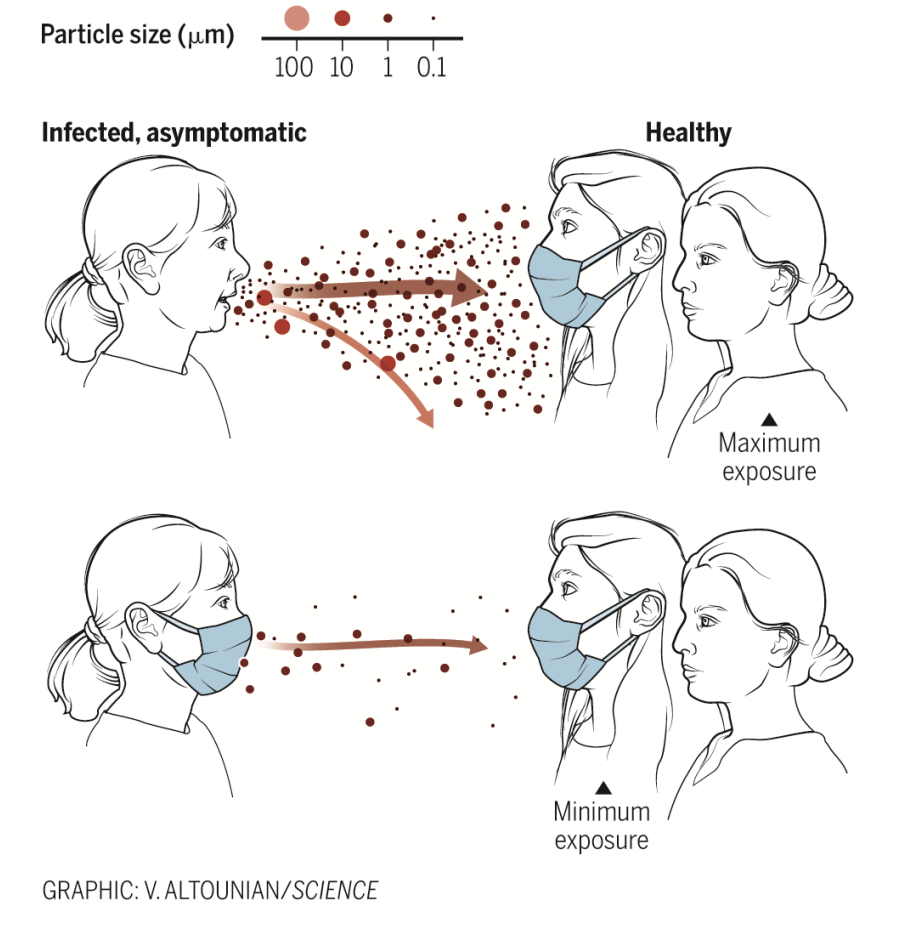
Mode Of Transmission
Person-to-person transmission
The virus is thought to spread mainly from person-to-person.
- Between people who are in close contact with one another (within about 6 feet).
- Through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes. These droplets can land in the mouths or noses of people who are nearby or possibly be inhaled into the lungs.
Transmission from contact with infected surfaces or objects
It may be possible that a person can get COVID-19 by touching a surface or object that has the virus on it and then touching their own mouth, nose, or possibly their eyes, but this is not thought to be the main way the virus spreads.
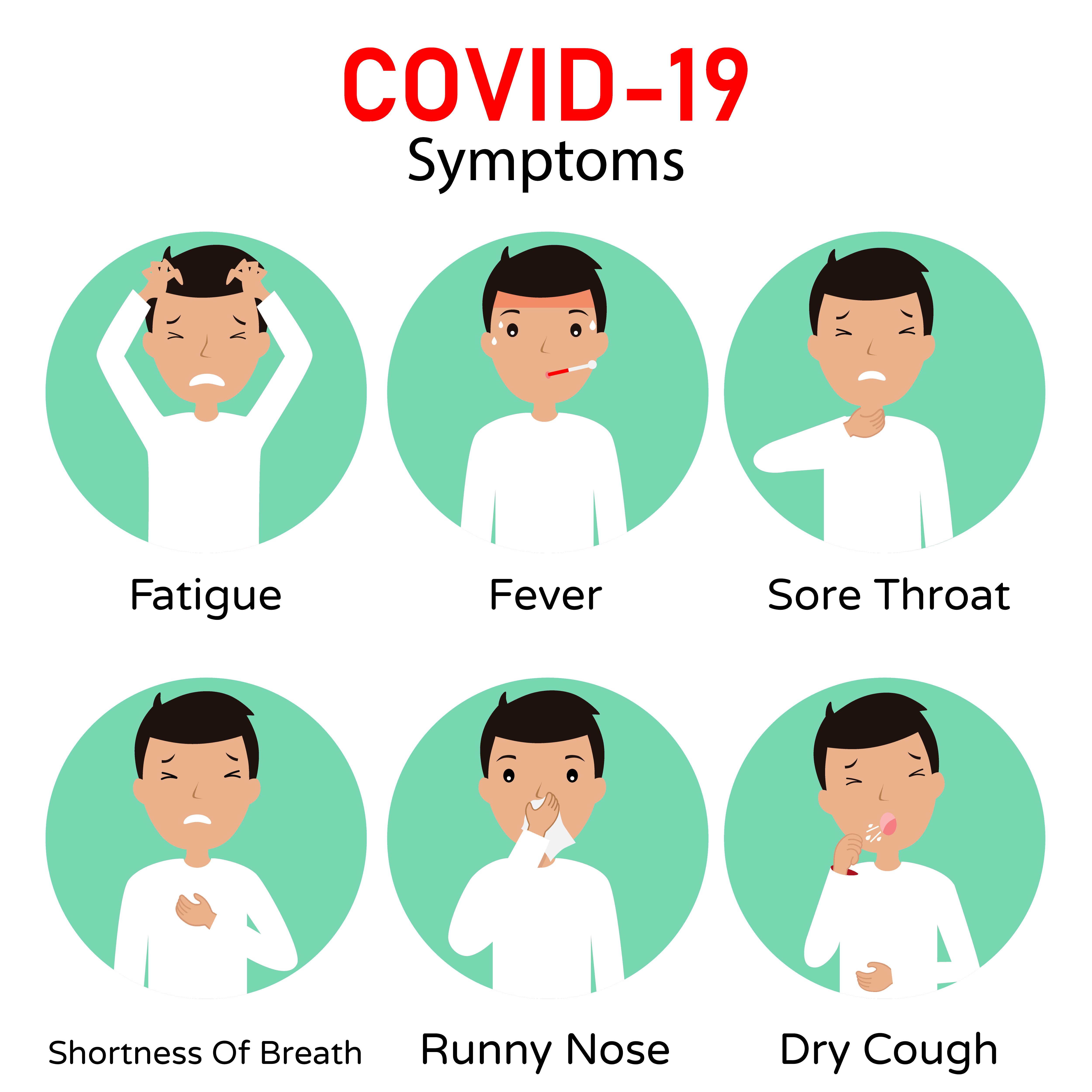
Illnesses
Reported illnesses have ranged from mild symptoms to severe illness and death for confirmed (COVID-19) cases.
Common symptoms that may appear 1-14 days after exposure are:
- Fever
- Dry cough
- Shortness of breath
- Generalized fatigue
If you have been exposed to an individual diagnosed with COVID-19 in the past 14 days, or you have any of the above symptoms we recommend you take our assessment and speak to one of our doctors. See A Doctor Online
COVID-19 – Prevention & Personal Hygiene
COVID-19 – Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a coronavirus?
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses which may cause illness in animals or humans. In humans, several coronaviruses are known to cause respiratory infections.
2. What is COVID-19?
COVID-19 is the infectious disease caused by the most recently discovered coronavirus. This new virus and disease were unknown before the outbreak began in Wuhan, China, in December 2019.
3. What are the symptoms of COVID-19?
The most common symptoms of COVID-19 are fever, tiredness, and dry cough. Some patients may have aches and pains, nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat or diarrhea. These symptoms are usually mild and begin gradually.
4. How does COVID-19 spread?
People can catch COVID-19 from others who have the virus. The disease can spread from person to person through small droplets from the nose or mouth which are spread when a person with COVID-19 coughs or exhales. These droplets land on objects and surfaces around the person. Other people then catch COVID-19 by touching these objects or surfaces, then touching their eyes, nose or mouth.
5. What can I do to protect myself and prevent the spread of disease?
You can reduce your chances of being infected or spreading COVID-19 by taking some simple precautions:
- Regularly and thoroughly wash you hands with soap and water or clean them with an alcohol based sanitizer.
- Maintain at least 1 metre (3 feet) distance between yourself and anyone who is coughing or sneezing.
- Avoid touching eyes, nose and mouth.
- Make sure you, and the people around you, follow good respiratory hygiene. This means covering your mouth and nose with your bent elbow or tissue when you cough or sneeze.
- Stay home if you feel unwell. If you have a fever, cough and difficulty breathing, seek medical attention and call in advance.
- Stay informed on the latest developments about COVID-19. Follow advice given by your healthcare provider.
6. How likely am I to catch COVID-19?
The risk depends on where you are – and more specifically, whether there is a COVID-19 outbreak unfolding there. If you exercise social distancing and strict personal hygiene the risk of catching COVID-19 will be low.
7. Should I worry about COVID-19?
Illness due to COVID-19 infection is generally mild, especially for children and young adults. However, it can cause serious illness: about 1 in every 5 people who catch it need hospital care. It is therefore quite normal for people to worry about how the COVID-19 outbreak will affect them and their loved ones.
8. Who is at risk of developing severe illness?
While we are still learning about how COVID-2019, older persons and persons with pre-existing medical conditions (such as high blood pressure, heart disease, lung disease, cancer or diabetes) appear to develop serious illness more often than others.
9. Are antibiotics effective in preventing or treating the COVID-19?
No. Antibiotics do not work against viruses, they only work on bacterial infections. COVID-19 is caused by a virus, so antibiotics do not work.
10. Is there a vaccine, drug or treatment for COVID-19?
Not yet. To date, there is no vaccine and no specific antiviral medicine to prevent or treat COVID-2019. However, those affected should receive care to relieve symptoms. People with serious illness should be hospitalized. Most patients recover thanks to supportive care. Possible vaccines and some specific drug treatments are under development.
11. Is COVID-19 the same as SARS?
No. The virus that causes COVID-19 and the one that causes Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) are related to each other genetically, but they are different. SARS is more deadly but much less infectious than COVID-19.
12. Should I wear a mask to protect myself?
Only wear a mask if you are ill with COVID-19 symptoms (especially coughing) or looking after someone who may have COVID-19.
13. How long is the incubation period for COVID-19?
The “incubation period” means the time between catching the virus and beginning to have symptoms of the disease. Most estimates of the incubation period for COVID-19 range from 1-14 days.
14. Can humans become infected with the COVID-19 from an animal source?
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that are common in animals. Occasionally, people get infected with these viruses which may then spread to other people. Possible animal sources of COVID-19 have not yet been confirmed.
15. How long does the virus survive on surfaces?
It is not certain how long the virus that causes COVID-19 survives on surfaces, but it seems to behave like other coronaviruses. Studies suggest that coronaviruses may persist on surfaces for a few hours or up to several days.
16. Is it safe to receive a package from any area where COVID-19 has been reported?
Yes. The likelihood of an infected person contaminating commercial goods is low and the risk of catching the virus that causes COVID-19 from a package that has been moved, travelled, and exposed to different conditions and temperature is also low.
17. Is there anything I should not do?
The following measures ARE NOT effective against COVID-2019 and can be harmful:
- Smoking
- Taking traditional herbal remedies
- Wearing multiple masks
- Taking self-medication such as antibiotics
In any case, if you have fever, cough and difficulty breathing seek medical care early to reduce the risk of developing a more severe infection and be sure to share your recent travel history with your health care provider.